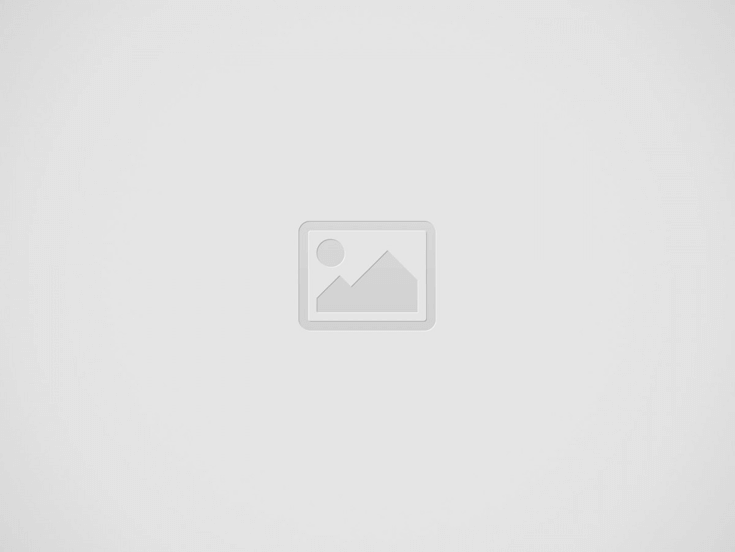

| Difficult Word/ Phrase | Contextual Sense |
| Dilute | Reduced in strength |
| Hasty | Done quickly and without due deliberation |
| Allegation | a formal accusation against somebody (often in a court of law) |
| Stringent | Demanding strict attention to rules and procedures |
| Promulgate | Put a law into effect by formal declaration |
| Nepotism | Favouritism shown to relatives or close friends by those in power |
| Implication | the act of suggesting something without saying it directly |
| Envisage | Form a mental image of something that is not present or that is not the case |
| Strike down | Declare null and void; make ineffective |
| Dispose of | Deal with or settle |


Wrong route: On Kerala Lok Ayukta law
Kerala’s move to dilute (Reduced in strength) the Lok Ayukta law through an ordinance is questionable
The Kerala government’s proposal to amend its Lok Ayukta Act through an ordinance appears questionable and hasty (Done quickly and without due deliberation). Even though the Left Democratic Front (LDF) government is citing legal opinion to justify the proposed amendments, it does give an impression that it is in an unseemly hurry to remove the finality attached to a provision that allows the anti-corruption judicial body to direct a public servant to vacate office, if an allegation (a formal accusation against somebody (often in a court of law)) is substantiated. The criticism by the Opposition that the change may dilute the Lok Ayukta law appears valid, as Section 14 of the Lok Ayukta Act is its most stringent (Demanding strict attention to rules and procedures) provision. Both the Congress-led United Democratic Front and the BJP have appealed to the Governor not to promulgate (Put a law into effect by formal declaration) the ordinance cleared by the Cabinet. Opposition parties have suggested that the proposal may be linked to ongoing inquiries by the Lok Ayukta against members of the Cabinet. Also, the present regime has been adversely affected by this particular provision. In April 2021, Minister for Higher Education and Minority Welfare K.T. Jaleel had to resign after the Lok Ayukta found him guilty of nepotism (Favouritism shown to relatives or close friends by those in power). The present regime seems to have realised only after this episode the implications (the act of suggesting something without saying it directly) of the binding nature of the Lok Ayukta’s ‘declaration’ that a public servant, against whom an allegation is substantiated, should not continue to hold office. It is strange that the Government now says the section is unconstitutional when it could have been challenged by Mr. Jaleel himself.
The Government has defended the proposed ordinance on the ground that the section amounts to removal of a Minister duly appointed by the Governor on the advice of the Chief Minister, and violates Articles 163 and 164 of the Constitution. Further, there is no provision for appeal. It proposes to amend it to the effect that the Governor, the government or authority may decide on the Lok Ayukta’s finding within three months. It also seeks to provide for an appeal. While these are valid points, there is room to question the adoption of the ordinance route. It is also curious that the provision is now considered unconstitutional when it was an earlier LDF regime headed by E.K. Nayanar that enacted the law in 1999. The legislation was quite ahead of its time, as it envisaged (Form a mental image of something that is not present or that is not the case) removal of a public servant from office following an adverse judicial finding long before the Supreme Court paved the way for automatic disqualification of an elected representative upon conviction. It was only in 2013 that the apex court struck down (Declare null and void; make ineffective) a clause in election law that saved a serving legislator from disqualification following conviction until an appeal was filed and disposed of (Deal with or settle). A regime truly disposed towards corruption-free governance should not normally be worried about a law that allows an independent judicial forum to direct a public servant to leave office. If it has well-founded reservations about the process, it should not be chary of introducing relevant amendments in the Assembly.
Keep your vocabulary updated with the help of our articles where we highlight 10 difficult words/ phrases and explain their contextual sense.
Recent Posts
Career Growth and Promotions for RBI Grade B Officers
Learn about the career growth and promotion structure for RBI Grade B officers and how…
300+ Reasoning Important Questions For BOB Apprentice 2025 Exam
In this article we are providing the 300+ Reasoning Important Questions For the BOB Apprentice…
Step-by-Step Preparation Strategy for PNB SO 2025 Exam
In this article we are providing the Step-by-Step Preparation Strategy for PNB SO 2025 Exam,…
IBPS PO Syllabus 2025, Check Prelims & Mains Detailed Syllabus
IBPS PO Syllabus 2025 will be released along with a notification pdf. Candidates can check…
What is the probation period for RBI grade B officers?
Learn about the RBI Grade B probation period, its importance, and how it shapes officers'…
IBPS SO Syllabus 2025, Check Prelims & Mains Pattern and Syllabus
IBPS SO Syllabus 2025 will be released on the official website. Candidates can check Prelims…


