SBI PO 2024 Most Scoring Topics For Reasoning: The State Bank of India conducts the SBI PO exam to recruit candidates for the post of Probationary Officer. The SBI PO prelims exam consists of three sections English Language, Numerical Ability, and Reasoning Ability. Among all the sections, the reasoning ability section is considered one of the highest-scoring sections. But it requires a lot of study, practice, and much more. One can easily score good marks if he/she knows the important topics. Candidates can set their priorities for those topics and can focus on them to increase their chances of scoring well in the exam. In this blog, we have provided the SBI PO 2024 most scoring topics for the reasoning section. Candidates who are going to prepare for the exam must read this blog carefully.
SBI PO Prelims Topic-Wise Weightage for Reasoning Section
Below we have provided the SBI PO prelims topic-wise weightage for reasoning ability section. This topic-wise weightage will help the candidates in prioritizing the topics into strong and weak areas.
| SBI PO Prelims Topic-Wise Weightage for Reasoning Section | |||||
| Topics | Weightage 2023 | Weightage 2022 | Weightage 2021 | Weightage 2020 | Weightage 2019 |
| Puzzles & Seating Arrangement | 18-25 | 15-33 | 15-28 | 15-24 | 15-25 |
| Syllogism | 2-6 | 3-4 | 4-5 | 3-4 | 5 |
| Inequality | 3-5 | 2-5 | 0-5 | – | 0-2 |
| Coding Decoding | 0-5 | 0-5 | 1-5 | 0-3 | 0-5 |
| Alphanumeric Series | – | – | 5 | 0-2 | 0-2 |
| Direction | 1-3 | 0-3 | 0-3 | 0-3 | 0-4 |
| Blood Relation | 2-4 | 0-4 | 0-3 | 0-4 | 0-4 |
| Order & Ranking | – | 0-2 | 0-2 | – | 0-4 |
| Miscellaneous | 1-8 | 1-5 | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-4 |
SBI PO Most Scoring Topics For Reasoning Section
Below we have provided the basics of the SBI PO most scoring topics for the reasoning ability section. Before solving and practicing the questions candidates must understand the basics of the topics of reasoning ability section. This will help them in understanding the questions easily.
1. Puzzle and Seating Arrangement
Solving puzzles and questions related to the seating arrangements belong to the Reasoning Ability section. The SBI presents these types of questions to measure the capacity of candidates like how they put information into perspectives and their critical reasoning skills. Some of the questions are linear forms, circular forms, and other forms. To master such types of topics one should engage with different types of questions. To assemble the solution you should use diagrams for the analysis of the given clues to placing them. Approaching each of these pieces systematically will show you the kind of patterns that are likely to emerge and therefore, the most effective methods to solving each of them.
2. Syllogisms
Syllogisms are the types of questions in which candidates are provided some statements and conclusions. Based on statements and conclusions they have to choose options such as which conclusion is correct. They commonly entail deducing an outcome based on certain hypotheses and are best illustrated using Venn diagrams. Other concepts that need to be explained are different types of statements like universal affirmative, particular negative, and so on. Candidates are advised to use the technique of eliminating wrong answers. But they must ensure to do this fast, this will help them in saving a lot of time during the test.
3. Blood Relations
Blood relations questions are the types of questions where candidates are required to solve questions based on relations. They have to deduce relations within a certain family or of a certain kind. These questions can range from the simplest relation (as siblings and parents) to that of a distant relation with your cousins or grandparents. When solving these questions, candidates are advised to draw a family tree or a diagram that would illustrate the relations. This will help them to understand the relations between close and distant relation easily and they will be able to answer the questions.
4. Input-Output
The SBI asks questions from input-output topics to assess your skills in pattern or sequence recognition. Such questions refer to a sequence of operations that may be performed on figures or Latin letters in one or another order. They include problems in a way where an arrangement of digits or letters may be reordered according to a certain pattern. On this topic, try to practice all kinds of questions. This will give you an understanding of different patterns. By solving many questions based on input and output, one can increase the number of questions solved in the least time possible with fewer mistakes.
5. Direction Based Questions
Direction-based tests check your spatial orientation and your ability to solve logical problems relating to movement in various directions. Some questions may require you to guess positions after a set of movements have been made for instance north, south, east, and west. As preparation, candidates are advised to first perform imagination of the moves and draw simple charts or maps to simplifies the question. The ability to easily understand and visualize these movements will boost the speed of solving the problems. In this way when you sit down to do your practice you will be in a position to handle direction-based questions with ease within a limited amount of time.
6. Coding-Decoding
Coding-decoding questions test your capacity to decode written messages or symbols to letters and numbers. Candidates must solve questions based on particular operations such as moving, reversing, or substituting letters in a word or phrase. Different types of questions come under this topic. Practice many problems on this topic by which you can gain confidence and able to solve all types of questions. As you practice through many coding questions, whether easy or challenging it will take less time if you recognize some of the patterns in coding.
7. Series Completion
It tests your capacity to complete patterns of sequences or find the odd one out within a group. The last questions in a series may be numbers or letters in which one is expected to guess the next item for a certain pattern. Odd one-out questions are those where you are tested on your ability to identify which item in a group is different from the others. When it comes to these topics, more emphasis should be placed on pattern recognition, including arithmetical or geometrical progression for number sequences, and more focused on the identification of that number that does not fit. SBI can present these questions in different ways, so candidates are advised to solve questions on this topic as much as possible.
Practice Sample Questions On Reasoning Ability Section
Directions (1-2): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
There are 11 boxes of different colors i.e. Red, Black, Yellow, Green, Purple, Blue, Grey, Pink, White, Violet, and Silver which are kept one above the other. The bottommost box is numbered 1 and the topmost box is numbered 11.
Blue color box is three boxes above the Purple color box and neither of them is a prime numbered box. Silver color box is two boxes above the Green color box. Number of boxes above the Blue color box is equal to the number of boxes below the Green colored box. White color box is at most three boxes above Red colored box. There are at least three boxes between the Silver color box and the Black colored box. Yellow colored box is kept immediately below the Black colored box but is not box 2. The Violet colored box is two boxes above the Grey colored box but not the topmost box. Pink color box is below box 6.
Starting Point: As Blue colored box is three boxes above Purple colored box and neither of them is a prime numbered box which means Blue colored box is placed either on box no. 9 or 4.
Clues: Silver colored box is two boxes above Green colored box. No. of boxes above Blue colored box is equal to the no. of boxes below Green colored box.
Inference: So, there are either two or seven boxes above the Blue colored box which is equals to the number of boxes below the box which is of Green colored box.
Case I: When Blue colored box is numbered as 4:
| Box Number | Box Color |
| 11 | |
| 10 | Silver |
| 9 | |
| 8 | Green |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | Blue |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | Purple |
Case II: When Blue colored box is numbered as 9:
| Box Number | Box Color |
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 9 | Blue |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | Purple |
| 5 | Silver |
| 4 | |
| 3 | Green |
| 2 | |
| 1 |
Clues: There are at least three boxes between the Silver color box and Black colored box. Yellow colored box is immediately below Black colored box but is not box 2. Violet colored box is two boxes above Grey colored box but not the topmost box, Pink colored box is below box 6. White colored box is at most three boxes above Red colored box,
Inference: So, Yellow colored box is placed immediately below the Black colored box but not as box numbered 2 which is not possible in case I so, case I is rejected. And Pink colored box is placed below the box number 6 which means Pink colored box is placed at the bottom and White colored box is box 8 and Red colored box is box 7.
The final table is given below:
| Box Number | Box Color |
| 11 | Black |
| 10 | Yellow |
| 9 | Blue |
| 8 | White |
| 7 | Red |
| 6 | Purple |
| 5 | Silver |
| 4 | Violet |
| 3 | Green |
| 2 | Grey |
| 1 | Pink |
Question 1: Which box is the bottommost box?
A) Pink box
B) Green box
C) Blue box
D) Yellow box
E) None of the above
Solution:
Pink colored box is the bottommost box.
Hence, option a.
Question 2: How many boxes are placed above the Red colored box?
A) Three
B) Five
C) Two
D) Four
E) None of the above
Solution:
There are four boxes above the Red colored box.
Hence, option d.
Directions (3-4): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
Eight buses M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T are parked in a bus terminal. These buses are parked in a horizontal row such that equal number of buses is facing north and south.
Bus M is immediate left of bus S and both buses face north direction. Bus R is immediate left of bus Q, which is third bus from one of the extreme ends. There are three buses between bus P and bus Q, which is not adjacent to bus S. Bus P, bus R and bus Q face in same direction. Bus O is to the right of bus T but not at any extreme end. Bus T is adjacent to neither bus P nor bus O.
Starting Point: Here, we can start with bus P, bus Q and bus R in order to form two cases initially.
Clues:
1.) There are three buses between bus P and bus Q, which is not adjacent to bus S.
2.) Bus P, bus R and bus Q face in same direction.
3.) Bus R is immediate left of bus Q, which is third bus from one of the extreme ends.
4.) Bus M is immediate left of bus S and both buses face north direction.
Inference:
From (2), (3) and (4), bus P, bus R and bus Q face in south direction. From (1) and (4), bus M must be immediate left of bus P or bus R.
Case 1:
| P(South) | M(North) | S(North) | Q(South) | R(South) |
Case 2:
| Q(South) | R(South) | M(North) | S(North) | P(South) |
Clues:
5.) Bus O is to the right of bus T but not at any extreme end.
6.) Bus T is adjacent to neither bus P nor bus O.
7.) Equal number of buses is facing north and south.
Inference:
From (5) and (6), case 2 must be rejected as bus T cannot be placed in the arrangement. From (7), bus N and bus O face north direction.
Case 1:
| N(North) | P(South) | M(North) | S(North) | O(North) | Q(South) | R(South) | T(South) |
Question 3: Which of the following buses are immediate neighbours of bus R?
A) P, T
B) N, T
C) Q, T
D) P, M
E) N, S
Solution:
Bus Q and bus T are immediate neighbours of bus R.
Hence, option c.
Question 4: Which bus is third to the right of bus N?
A) Bus O
B) Bus T
C) Bus Q
D) Bus S
E) None of the above
Solution:
Bus S is third to the right of bus N.
Hence, option d.
Directions (5-6): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
In a certain language,
I. ‘our world is related’ is coded as ‘five four six one’
II. ‘related in way complex’ is coded as ‘two three seven one’
III. ‘world can be’ is coded as ‘five nine ten’
IV. ‘way to our complex’ is coded as ‘two eight six three’
From statement I and II, we conclude that “related” is coded as “one”
From statement I and IV, we conclude that “our” is coded as “six”
From statement I and III, we conclude that “world” is coded as “five”
From statement I alone, we conclude that “is” is coded as “four”
From statement II and IV, we conclude that “way” and “complex” are coded as “two” and “three”, but not necessarily in the same order.
From statement III, we conclude that “can” and “be” are coded as “nine” and “ten”, but not necessarily in the same order.
From statement II alone, we conclude that “in” is coded as “seven”
From statement IV alone, we conclude that “to” is coded as “eight”
The final table is shown below:
| Word | our | world | is | related | in | way | complex | can | be | to |
| Code | six | five | four | one | seven | two/three | three/two | nine/ten | ten/nine | eight |
Question 5: What is the code of the word “world”?
A) Five
B) Four
C) Six
D) One
E) None of the above
Solution:
The word “world” is coded as “five”.
Hence, option a.
Question 6: Which of the following word is coded as “eight”?
A) way
B) to
C) our
D) complex
E) None of the above
Solution:
The word “to” is coded as “eight”.
Hence, option b.
Directions (7-8): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
Point J is 3m south of point K, which is 5m west of L. Point M is 3m west of point N, which is 2m south of point O. Point M is 2m north of point L. Point P is 9m north of point Q, which is 8m west of point R. Point O is 11m east of point P.
We draw the following figure:
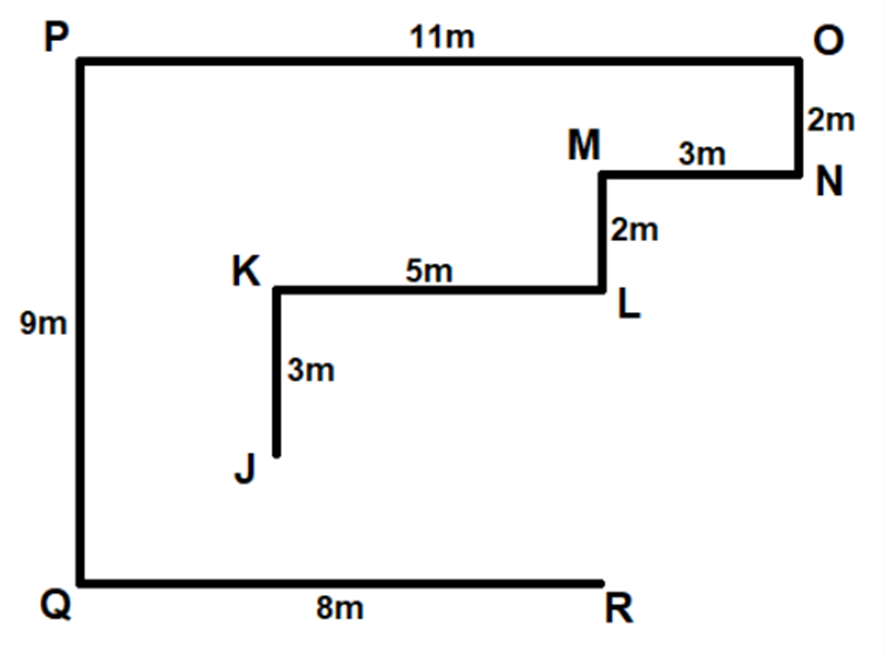
Question 7: What is the shortest distance between point R and point L?
A) 3m
B) 4m
C) 5m
D) 6m
E) None of the above
Solution:
The shortest distance between point R and point L is 5m.
Hence, option c.
Question 8: What is the direction of point J with respect to point Q?
A) South-east
B) South-west
C) North-west
D) North-east
E) None of the above
Solution:
Point J is in north-east of point Q.
Hence, option d.
Question 9: How many such pair(s) of letters are in the word “PERMUTATION” which has as many letters between them (both forward and backward) as in the English alphabetical series?
A) Four
B) Two
C) None
D) Three
E) None of the above
Solution:
Given word:
PERMUTATION
There are five such pairs (PR), (PM), (UT), (EN) and (ON), which have as many letters between them (both forward and backward) as in the English alphabetical series.
Hence, option e.
Question 10: In the question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion (s) among given three conclusions is /are definitely true and then give your answer accordingly.
Statements: L > M = T = O, O > E = F ≥ G ≥ H > I
Conclusions:
I. M > I
II. E = H
III. E > I
A) Only Conclusion I is true
B) Only Conclusion II is true
C) Only Conclusion I and II are true
D) Only Conclusion III is true
E) Only Conclusion I and III are true
Solution:
Given statements: L > M = T = O, O > E = F ≥ G ≥ H > I
On combining the given statements, we get:
L > M = T = O > E = F ≥ G ≥ H > I
Conclusions:
I. M > I: True (As M = T = O > E = F ≥ G ≥ H > I, so, M > I).
II. E = H: False (As E = F ≥ G ≥ H, so, E ≥ H).
III. E > I: True (As E = F ≥ G ≥ H > I, so, E > I).
Only Conclusion I and III are true.
Hence, option e.
Other Related Blogs on SBI PO 2024
| SBI PO Exam Pattern 2024 | SBI PO Syllabus 2024 |
| SBI PO Salary 2024 | SBI PO Cut Off 2024 |
| SBI PO Study Plan 2024 | SBI PO Preparation Strategy 2024 |
SBI PO 2024 Most Scoring Topics For Reasoning Section FAQs
Important reasoning topics include puzzle, classification, series, coding-decoding, syllogism, seating arrangement, etc.
Candidates can find the basic knowledge of the most scoring topics for the reasoning section in this blog.
- Sign Up on Practicemock for Updated Current Affairs, Topic Tests and Mini Mocks
- Sign Up Here to Download Free Study Material
Free Mock Tests for the Upcoming Exams
- IBPS PO Free Mock Test
- RBI Grade B Free Mock Test
- IBPS SO Free Mock Test
- NABARD Grade A Free Mock Test
- SSC CGL Free Mock Test
- IBPS Clerk Free Mock Test
- IBPS RRB PO Free Mock Test
- IBPS RRB Clerk Free Mock Test
- RRB NTPC Free Mock Test
- SSC MTS Free Mock Test
- SSC Strenographer Free Mock Test
- GATE Mechanical Free Mock Test
- GATE Civil Free Mock Test
- RRB ALP Free Mock Test
- SSC CPO Free Mock Test
- AFCAT Free Mock Test
- SEBI Grade A Free Mock Test
- IFSCA Grade A Free Mock Test
- RRB JE Free Mock Test
- Free Banking Live Test
- Free SSC Live Test



