Mensuration For SSC CGL Exam: Mensuration is one of the topics that can be asked in many government exams. Candidates can expect at least 2-3 mensuration questions at the difficulty level of easy to moderate in the SSC CGL Exam. Mensuration is a type of topic that belongs to quantitative aptitude and is used in daily life. In this blog, we have provided the basic concept of Mensuration and the formulas. We have also provided the questions on mensuration in both Hindi and English, along with the answers and their detailed solutions. Candidates are advised to understand the basics first and then try to solve the questions.
Mensuration for SSC CGL: Topic-wise and Complete Preparation
Solving the topic test is very important if you want to get in-depth knowledge of the individual topic. Below, we have provided the topic tests for each section, including quizzes for current affairs, previous year question papers, and full-length mock tests.
| Click For Mock Test – > | SSC CGL Free Full-Length Mock Test |
| Click For SSC CA – > | SSC CGL Free Weekly Current Affairs Tests |
| Click For Quant – > | Quantitative Aptitude Free Topic Tests |
| Click For Reasoning – > | General Reasoning Free Topic Tests |
| Click For English – > | English Comprehension Free Topic Tests |
| Click For SSC GA – > | General Awareness Free Topic Tests |
| Click For Sectional Mock Tests -> | SSC CGL Free Sectional Mock Tests |
| Click For PYQs – > | Free SSC CGL Previous Year Question Papers |
Mensuration for SSC CGL
Mensuration is a mathematical concept that deals with the measurement of figures and shapes such as length, width, height, area, perimeter, etc.
Formulas of Mensuration For 2D Shapes:
Rectangle:

- Area of Rectangle = Length × Breadth.
- Perimeter of a Rectangle = 2 × (Length + Breadth)
- Length of the Diagonal = √(Length2 + Breadth2)
Square:

- Area of a Square = Length × Length = (Length)2
- Perimeter of a square = 4 × Length
- Length of the Diagonal = √2 × Length
Parallelogram:

- Area of a Parallelogram = Length × Height
- Perimeter of a Parallelogram = 2 × (Length + Breadth)
Triangle:
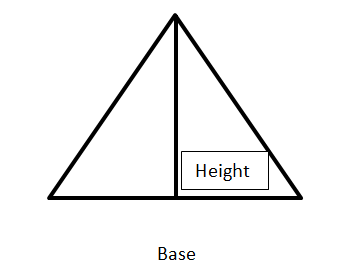
- Area of a triangle=(1/2)(Base × Height)
For a triangle with sides measuring a, b and c, respectively:

- Perimeter = a + b + c
- s = semi perimeter = perimeter/2 = (a+b+c)/2
- Area of Triangle,
Trapezium:

- Area of a trapezium = (1/2) × (sum of parallel sides) × (distance between parallel sides)
= (1/2) × (AB+DC) × AE - Perimeter of a Trapezium = Sum of All Sides
Rhombus:
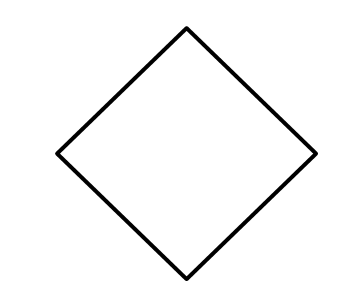
- Area of a rhombus=(1/2)×Product of diagonals
- Perimeter of a rhombus = 4 × l
Mensuration Formulas For 3D Shapes
| Shape | Volume (Cubic units) | Curved Surface Area (CSA) or Lateral Surface Area (LSA) (Square units) | Total Surface Area (TSA) (Square units) |
| Cube | a3 | LSA = 4 a2 | 6 a2 |
| Cuboid | l × b × h | LSA = 2h (l + b) | 2 (lb +bh +hl) |
| Sphere | (4/3) π r3 | 4 π r2 | 4 π r2 |
| Hemisphere | (⅔) π r3 | 2 π r2 | 3 π r2 |
| Cylinder | π r2 h | 2π r h | 2πrh + 2πr2 |
| Cone | (⅓) π r2 h | π r l | πr (r + l) |
Mensuration SSC CGL Questions
Practice the different types of questions related to mensuration and find detailed solutions along with the explanation (provided in PDF).
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 1:
A solid metallic sphere of radius 26 cm is melted and recast into a cone having diameter of the base as 26 cm. What is the height of the cone?
A) 104 cm
B) 492 cm
C) 416 cm
D) 304 cm
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 2:
How many spheres each of radius 2.1 cm can be formed by melting a metallic cuboid if the length, breadth and height of the cuboid are 44.1 cm, 15 cm and 22 cm, respectively?
A) 380
B) 365
C) 350
D) 375
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 3:
The radius and height of right circular cylindrical pipe are 21 cm and 7 cm. Find the cost of overlaying the curved part of the pipe with aluminium sheet costing Rs. 2 per cm2
A) Rs. 1,848
B) Rs. 422
C) Rs. 844
D) Rs. 924
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 4:
A solid copper sphere of radius 9 cm is melted and moulded into a right circular cylindrical rod of radius 3 cm. What is the length of this rod?
A) 112 cm
B) 108 cm
C) 180 cm
D) 90 cm
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 5:
Base radius of a right circular cone is equal to the edge of a cube whose volume is equal to the 1728 m3. Find the height of the cone if slant height of the cone is 37 metres.
A) 35 metres
B) 37 metres
C) 32 metres
D) 34 metres
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 6:
Base area of a right circular cylinder is equal to the area of a rectangle having its length 6.6 cm. What will be the perimeter of the rectangle if radius of the cylinder is 2.1 cm? (Take π = )
A) 17.4 cm
B) 8.7 cm
C) 14.6 cm
D) 16.8 cm
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 7:
The radii of the ends of a frustum of a cone are 5 cm and 2 cm. Find the volume of frustrum if its height is 14 cm. (Use π = )
A) 548 cm3
B) 572 cm3
C) 458 cm3
D) 624 cm3
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 8:
The length of the edge of a cube is 6.3 cm. What will be the volume of the largest sphere that can be carved out from the cube? (Take π = )
A) 156.328 cm3
B) 130.977 cm3
C) 160.321 cm3
D) 172.324 cm3
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 9:
A rectangular water tank is 3 metres high, 6 metres long and 7 metres wide. How much water (in litres) can it hold?
A) 1,26,000
B) 1,44,000
C) 1,14,000
D) 1,26,00
Mensuration SSC CGL Question 10:
A solid metallic hemisphere of radius 6.3 cm is melted and recast into a right circular cylinder of radius 9 cm. What is the height (in cm, correct to one decimal place) of the cylinder?
A) 1.9
B) 2.1
C) 2.7
D) 2.5
Mensuration SSC CGL Questions FAQs
Candidates can expect at least 2-3 questions of mensuration for SSC CGL Exam.
The difficulty level of questions of Mensuration for SSC CGL Exam is easy to moderate.
Mensuration is a mathematical concept that deals with the measurement of figures and shapes such as length, width, height, area, perimeter, etc.
- Sign Up on Practicemock for Updated Current Affairs, Free Topic Tests and Free Mini Mocks
- Sign Up Here to Download Free Study Material
Free Mock Tests for the Upcoming Exams
- IBPS PO Free Mock Test
- RBI Grade B Free Mock Test
- IBPS SO Free Mock Test
- NABARD Grade A Free Mock Test
- SSC CGL Free Mock Test
- IBPS Clerk Free Mock Test
- IBPS RRB PO Free Mock Test
- IBPS RRB Clerk Free Mock Test
- RRB NTPC Free Mock Test
- SSC MTS Free Mock Test
- SSC Strenographer Free Mock Test
- GATE Mechanical Free Mock Test
- GATE Civil Free Mock Test
- RRB ALP Free Mock Test
- SSC CPO Free Mock Test
- AFCAT Free Mock Test
- SEBI Grade A Free Mock Test
- IFSCA Grade A Free Mock Test
- RRB JE Free Mock Test
- Free Banking Live Test
- Free SSC Live Test