One of the most important functions of a commercial bank is to grant loans and advances. Such loans and advances are given to members of the public and to the business community at a higher rate of interest than allowed by banks on various deposit accounts. The rate of interest charged on loans and advances varies according to the purpose and period of the loan and also the mode of repayment.
Loans
A loan is granted for a specific time period. Generally commercial banks provide short-term loans. But term loans, i.e., loans for more than a year may also be granted. The borrower may be given the entire amount in lump sum or in instalments. Loans are generally granted against the security of certain assets. A loan is normally repaid in instalments. However, it may also be repaid in lump sum.
Types Of Loans
Various types of loans are available in India, and they are classified based on two factor:
- Whether they require collateral
- The purpose they are used for
Based on whether they require collateral, loans are classified into secured loans and unsecured loans.
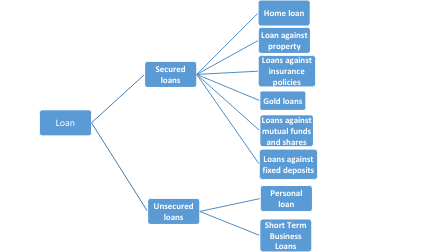
Secured loans: Secured loans are those which require collateral, i.e., borrowers have to provide an asset to the lender as security for the money you are borrowing. If the borrower is unable to repay the loan, the lender still has some means to get back their money.
The rate of interest of secured loans tends to be lower as compared to those for loans without collateral.
Types Of Secured Loans
1. Home loan: Home loans are a secured mode of finance that give you the funds to buy or build the home of your choice. Some type of home loans available in India are:
- Land purchase loan
- Home construction loan
- Home loan balance transfer
- Top up loan
The loan amount disbursed depends on borrower’s income, its stability and current liabilities etc.
2. Loan against property (LAP):
Loan against property is one of the most common forms of a secured loan where borrower can pledge any residential, commercial or industrial property for availing the funds required. The loan amount disbursed is equivalent to a certain percentage of the property’s value. While some lenders may offer an amount equivalent to 50-60% of the property’s value, others may offer an amount close to 80%. A loan against property helps in unlocking the dormant value of asset and can be used to satiate personal life goals such as higher education of children or marriage. Businesses use a loan against property for business expansion, R&D and product development etc.
3. Loans against insurance policies: A loan can also be availed against an insurance policy. However, all insurance policies don’t qualify for this, only endowment and money-back policies, which have a maturity value can be used to availing loans. Thus, a loan against a term insurance plan can’t be availed as it doesn’t have any maturity benefits. Also, loans can’t be availed against unit-linked plans as the returns aren’t fixed and depends on the performance of the market.
4. Gold loans: Gold has been one of the most favoured asset classes. According to a KPMG report, the organized Indian gold loan industry is expected to touch Rs. 3,101 billion by 2019-20. A gold loan requires you to pledge gold jewellery or coins as collateral. The loan amount sanctioned is a certain percentage of the gold’s value pledged. Gold loans are generally used for short-term needs and have a short repayment tenor compared to home loans and loan against property.
5. Loans against mutual funds and shares: Mutual funds can also be pledged as collateral for a loan. Equity or hybrid funds can be pledged to the financial institution for availing a loan. Generally, 60-70% of the value of units pledged can be availed as loan. Similarly, with shares, financial institutions create a lien against shares against which the loan is taken and the loan value is equivalent to a percentage of the value of the shares.
6. Loans against fixed deposits: Fixed deposit (FD) not only offers assured returns but can also be used for availing loan. The amount of loan can vary between 70-90% of the FD’s value and varies across lenders. However, it’s essential to note that the loan tenor can’t be more than the FD’s tenor.
II. Unsecured Loans
Unsecured loans are those which do not require collateral. The lender lends the money based on past associations, credit score and history. Thus, a borrower need to have a good credit history to avail these loans. Unsecured loans usually come at a higher rate of interest due to the lack of collateral.
Types Of Unsecured Loan
1. Personal loan: Personal loan is one of the most popular types of unsecured loans. However, since a personal loan is an unsecured mode of finance, the interest rates are higher compared to secured loans. A good credit score along with high and stable income ensures you can avail this loan at a competitive rate of interest. Personal loans can be used to cover a number of personal expenses such as:
- Manage all expenses of a family wedding
- Pay for a vacation or an international trip
- Finance your home renovation project
- Fund the cost of your child’s higher education
- Consolidate all your debts into a single loan
- Meet unexpected/ unplanned/ urgent expenses
2. Short-term business loans: A short-term business loan can be used to meet their expansion and daily expenses by various entities and organizations.
- Working capital loans
- Machinery loans and equipment finance
- Small business loans for MSMEs
- Loans for women entrepreneurs
- Loans for traders
- Loans for manufacturers
- Loans for service enterprises
Flexi Loans: Flexi loan is a new age loan that efficiently caters to the immediate financial requirement of customers. This loan is a type of personal loan in which lenders provide pre-approved loan limit to their customers which is credited to their bank account and can be utilized by them as and when required.
Based on their usage, loans are classified mainly into:
1. Education loans: An education loan is a sum of money borrowed to finance post-secondary education or higher education-related expenses. Education loans are intended to cover the cost of tuition, books and supplies, and living expenses while the borrower is in the process of pursuing a degree. The loan must repaid by the student once the course is complete. A unique feature of an education loan is the moratorium period, wherein the student has the option of not paying the EMIs until after 12 months of completing the course or 6 months after he/she starts working, whichever is earlier.
2. Vehicle loans: Vehicle loan helps to buy a particular vehicle and are offered either on purchase of a new vehicle or a used one.
Advances: An advance is a credit facility provided by the bank to its customers. It differs from loan in the sense that loans may be granted for longer period, but advances are normally granted for a short period of time. Further the purpose of granting advances is to meet the day-to-day requirements of business. The rate of interest charged on advances varies from bank to bank. Interest is charged only on the amount withdrawn and not on the sanctioned amount.
Types of Advances
Banks grant short-term financial assistance by way of cash credit, overdraft and bill discounting.
a) Cash Credit: Cash credit is an arrangement whereby the bank allows the borrower to draw amount upto a specified limit. The amount is credited to the account of the customer. The customer can withdraw this amount as and when he requires. Interest is charged on the amount actually withdrawn. Cash Credit is granted as per terms and conditions agreed with the customers.
b) Overdraft: Overdraft is also a credit facility granted by bank. Overdraft means the act of withdrawing more money from bank account than it has deposited in it. It is a temporary arrangement. Overdraft facility with a specified limit may be allowed either on the security of assets, or on personal security, or both.
c) Discounting of Bills: Banks provide short-term finance by discounting bills i.e. by making payment of the amount before the due date of the bills after deducting a certain rate of discount. The party gets the funds without waiting for the date of maturity of the bills. In case any bill is dishonored on the due date, the bank can recover the amount from the customer.
Important Terms Associated With Loan/Credit
- Pledge: It is when the property is offered as collateral or security. A pledged asset is a valuable asset that is transferred to a lender to secure a debt or loan. Pledged assets can reduce the down payment that is typically required for a loan. The asset may also provide a better interest rate or repayment terms for the loan. The borrower retains ownership of the assets and continues to earn interest or capital gains on those assets.
- Hypothecation: Hypothecation occurs when an asset is pledged as collateral to secure a loan. The owner of the asset does not give up title, possession, or ownership rights, such as income generated by the asset. However, the lender can seize the asset if the terms of the agreement are not met.
- Mortgage: A mortgage is a loan that the borrower uses to purchase or maintain a home or other form of real estate and agrees to pay back over time, typically in a series of regular payments. The property serves as collateral to secure the loan.
- Collateral: The term collateral refers to an asset that a lender accepts as security for a loan. Collateral may take the form of real estate or other kinds of assets, depending on the purpose of the loan. That is, if the borrower defaults on their loan payments, the lender can seize the collateral and sell it to recoup some or all of its losses. Collateral minimizes the risk for lenders.
- Assignment: An assignment is the transfer of an individual’s rights or property to another person or business. This concept exists in a variety of business transactions and is often spelled out contractually.
- Lien: A lien is a claim or legal right against assets that are typically used as collateral to satisfy a debt. A lien could be established by a creditor or a legal judgement. A lien serves to guarantee an underlying obligation, such as the repayment of a loan. If the underlying obligation is not satisfied, the creditor may be able to seize the asset that is the subject of the lien.
- Set–off: A set-off clause is a legal clause that gives a lender the authority to seize a debtor’s deposits when they default on a loan. A set-off clause can also refer to a settlement of mutual debt between a creditor and a debtor through offsetting transaction claims.
We hope that this PDF is going to be helpful in your preparation. Download other Static GK PDFs here.
Banking Free Mock Test
Credit Management & Lending Practices FAQ
Credit Management refers to the process of overseeing and controlling a company’s credit policies, ensuring that credit is extended responsibly, and managing the collection of outstanding debts.
Candidates download a free PDF on Credit Management & Lending Practices in the article below.
- Sign Up on Practicemock for Updated Current Affairs, Free Topic Tests and Free Mini Mocks
- Sign Up Here to Download Free Study Material
Free Mock Tests for the Upcoming Exams
- IBPS PO Free Mock Test 2024
- RBI Grade B Free Mock Test 2024
- IBPS SO Free Mock Test 2024
- NABARD Grade A Free Mock Test 2024
- SSC CGL Free Mock Test 2024
- IBPS Clerk Free Mock Test 2024
- IBPS RRB PO Free Mock Test 2024
- IBPS RRB Clerk Free Mock Test 2024
- RRB NTPC Free Mock Test 2024
- SSC MTS Free Mock Test 2024
- SSC Strenographer Free Mock Test 2024
- GATE Mechanical Free Mock Test 2024
- GATE Civil Free Mock Test 2024
- RRB ALP Free Mock Test 2024
- SSC CPO Free Mock Test 2024
- AFCAT Free Mock Test 2024
- SEBI Grade A Free Mock Test 2024
- IFSCA Grade A Free Mock Test 2024
- RRB JE Free Mock Test 2024
- Free Banking Live Test
- Free SSC Live Test



